
A brand new Linux rootkit malware known as Pumakit has been found that makes use of stealth and superior privilege escalation methods to cover its presence on programs.
The malware is a multi-component set that features a dropper, memory-resident executables, a kernel module rootkit, and a shared object (SO) userland rootkit.
Elastic Safety found Pumakit in a suspicious binary (‘cron’) add on VirusTotal, dated September 4, 2024, and reported having no visibility into who makes use of it and what it targets.
Usually, these instruments are utilized by superior risk actors concentrating on important infrastructure and enterprise programs for espionage, monetary theft, and disruption operations.
The Pumakit
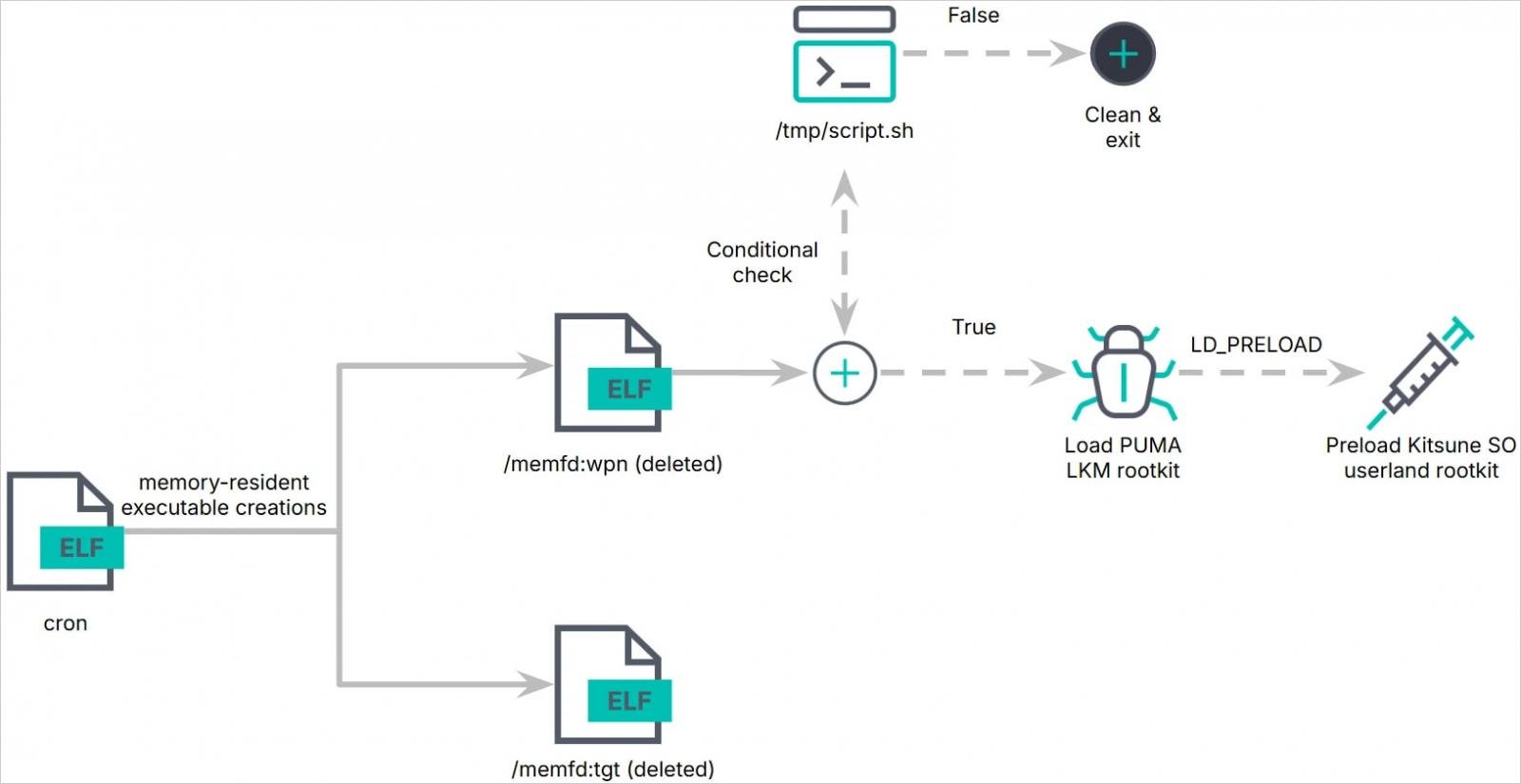
Pumakit employs a multi-stage an infection course of beginning with a dropper named ‘cron,’ which executes embedded payloads (‘/memfd:tgt’ and ‘/memfd:wpn’) totally from reminiscence.
The ‘/memfd:wpn’ payload, which executes in a baby course of, performs surroundings checks and kernel picture manipulation and finally deploys the LKM rootkit module (‘puma.ko’) into the system kernel.
Embedded throughout the LKM rootkit is Kitsune SO (‘lib64/libs.so’), performing because the userland rootkit that injects itself into processes utilizing ‘LD_PRELOAD’ to intercept system calls on the consumer degree.
Supply: Elastic Safety
Stealthy privilege escalation
The rootkit follows a conditional activation, checking for particular kernel symbols, safe boot standing, and different stipulations earlier than loading.
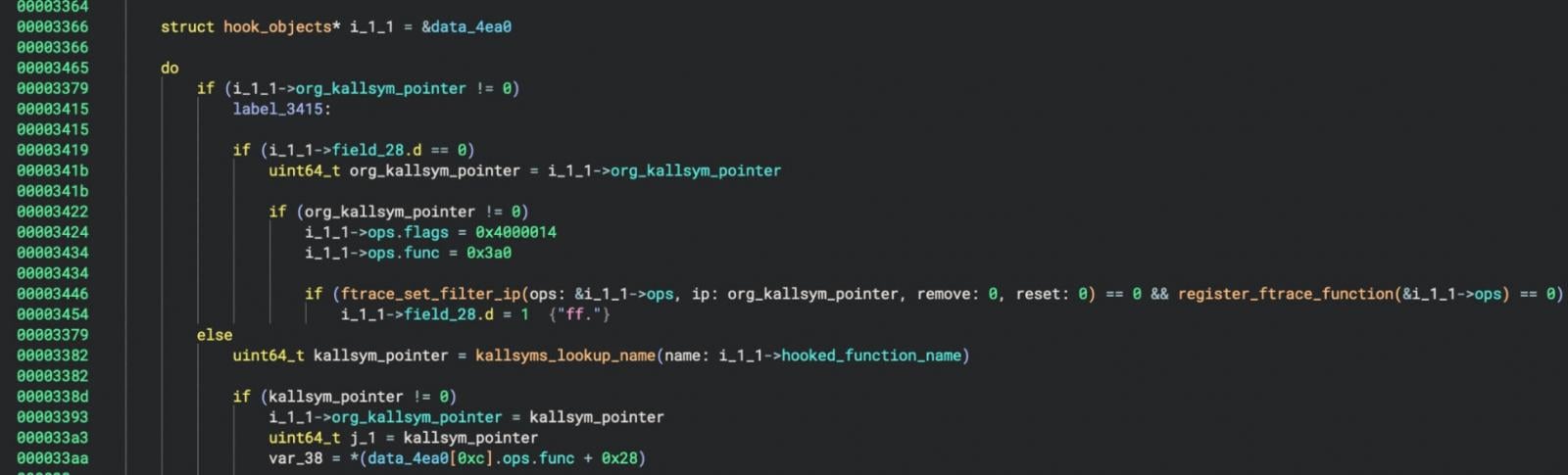
Elastic says Puma makes use of the ‘kallsyms_lookup_name()’ operate to govern system habits. This means the rootkit was designed to solely goal Linux kernels earlier than model 5.7, as newer variations now not export the operate and, subsequently, cannot be utilized by different kernel modules.
“The LKM rootkit’s capability to govern system habits begins with its use of the syscall desk and its reliance on kallsyms_lookup_name() for image decision,” explains Elastic researchers Remco Sprooten and Ruben Groenewoud.
“Not like trendy rootkits concentrating on kernel variations 5.7 and above, the rootkit doesn’t use kprobes, indicating it’s designed for older kernels.”
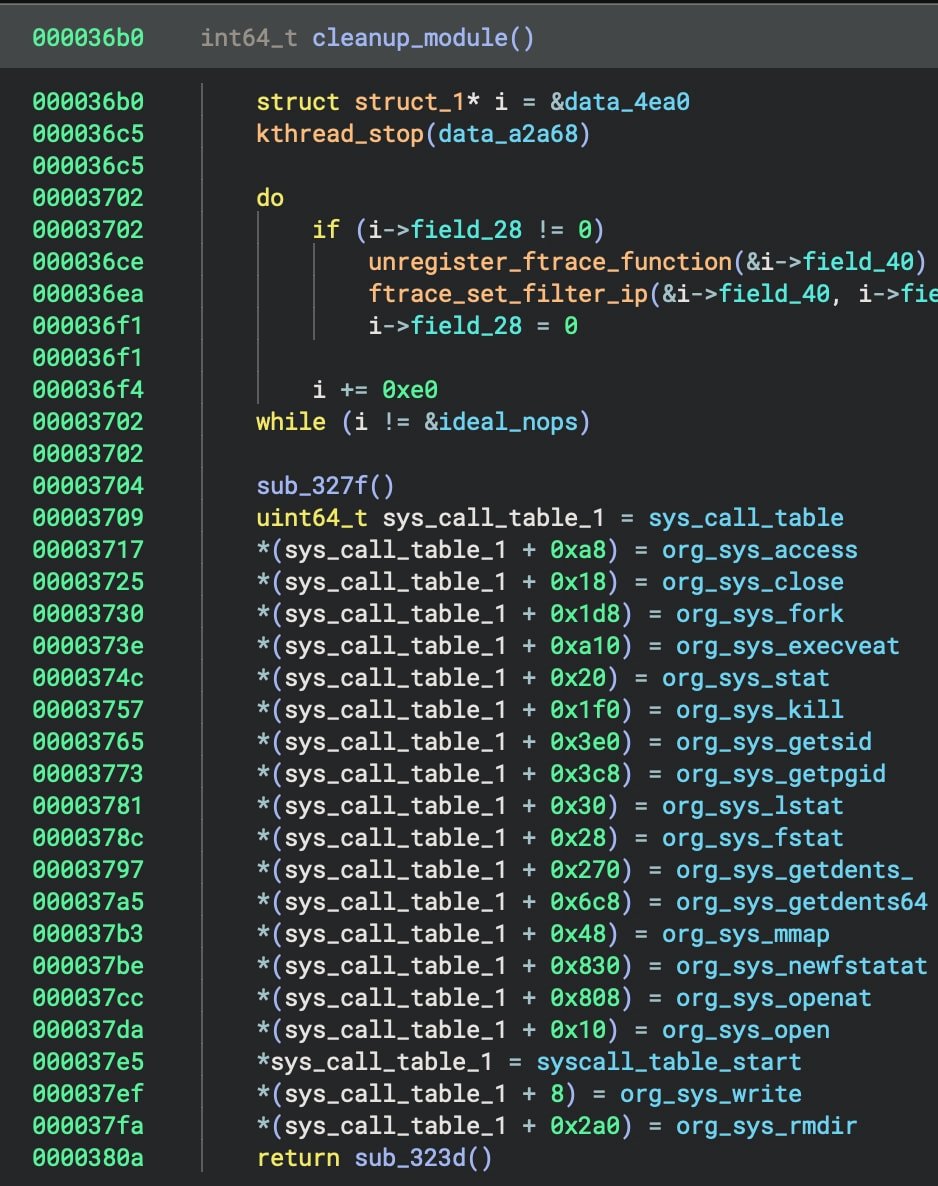
Puma hooks 18 syscalls and a number of kernel capabilities utilizing ‘ftrace,’ to realize privilege escalation, command execution, and the power to cover processes.
Supply: Elastic Safety
The kernel capabilities ‘prepare_creds’ and ‘commit_creds’ are abused to change course of credentials, granting root privileges to particular processes.
Supply: Elastic Safety
The rootkit can cover its personal presence from kernel logs, system instruments, and antivirus, and also can cover particular information in a listing and objects from course of lists.
If the hooks are interrupted, the rootkit reinitializes them, making certain that its malicious adjustments aren’t reverted and the module can’t be unloaded.
The userland rootkit Kitsune SO operates in synergy with Puma, extending its stealth and management mechanisms to user-facing interactions.
It intercepts user-level system calls and alters the habits of seems like ls, ps, netstat, high, htop, and cat to cover information, processes, and community connections related to the rootkit
It could actually additionally dynamically cover some other information and directories based mostly on attacker-defined standards and make malicious binaries totally invisible to customers and system admins.
Kitsune SO additionally handles all communications with the command and management (C2) server, relaying instructions to the LKM rootkit and transmitting configuration and system information to the operators.
Apart from file hashes, Elastic Safety has revealed a YARA rule to assist Linux system directors detect Pumakit assaults.