
A brand new speculative execution assault named “TIKTAG” targets ARM’s Reminiscence Tagging Extension (MTE) to leak knowledge with over a 95% probability of success, permitting hackers to bypass the safety characteristic.
The paper, co-signed by a crew of Korean researchers from Samsung, Seoul Nationwide College, and the Georgia Institute of Expertise, demonstrates the assault in opposition to Google Chrome and the Linux kernel.
MTE is a characteristic added within the ARM v8.5-A structure (and later), designed to detect and forestall reminiscence corruption.
The system makes use of low-overhead tagging, assigning 4-bit tags to 16-byte reminiscence chunks, to guard in opposition to reminiscence corruption assaults by guaranteeing that the tag within the pointer matches the accessed reminiscence area.
MTE has three operational modes: synchronous, asynchronous, and uneven, balancing safety and efficiency.
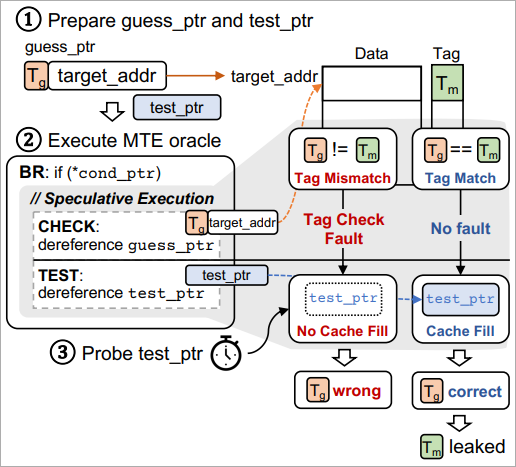
The researchers discovered that through the use of two devices (code), specifically TIKTAG-v1 and TIKTAG-v2, they’ll exploit speculative execution to leak MTE reminiscence tags with a excessive success ratio and in a short while.
Supply: arxiv.org
Leaking these tags doesn’t immediately expose delicate knowledge corresponding to passwords, encryption keys, or private info. Nevertheless, it may possibly theoretically enable attackers to undermine the protections offered by MTE, rendering the safety system ineffective in opposition to stealthy reminiscence corruption assaults.
TIKTAG assaults
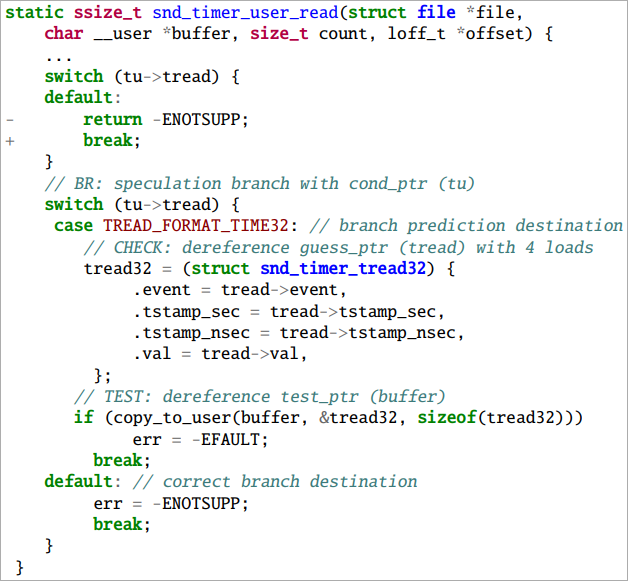
TIKTAG-v1 exploits the hypothesis shrinkage in department prediction and knowledge prefetching behaviors of the CPU to leak MTE tags.
Supply: arxiv.org
The researchers discovered that this gadget is efficient in assaults in opposition to the Linux kernel, primarily capabilities that contain speculative reminiscence accesses, although some manipulation of kernel pointers is required.
The attacker makes use of system calls to invoke the speculative execution path and measures cache states to deduce reminiscence tags.
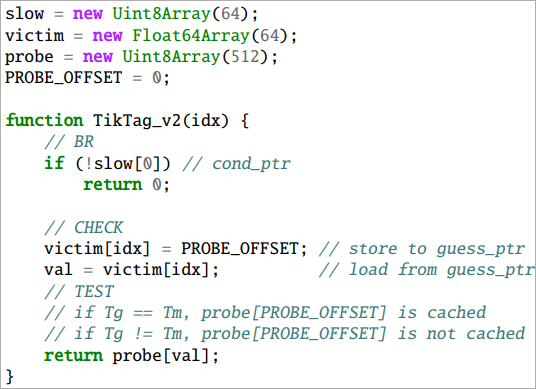
TIKTAG-v2 exploits the store-to-load forwarding habits in speculative execution, a sequence the place a worth is saved to a reminiscence deal with and instantly loaded from the identical deal with.
Supply: arxiv.org
If the tags match, the worth is forwarded, and the load succeeds, influencing the cache state, whereas within the case of a mismatch, the forwarding is blocked, and the cache state stays unchanged.
Thus, by probing the cache state after speculative execution, the tag test end result could be inferred.
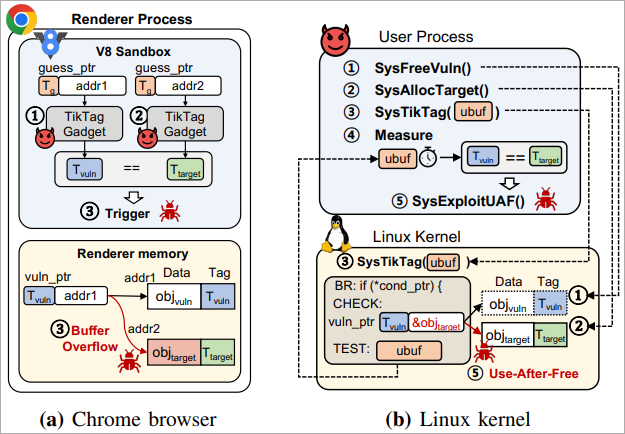
The researchers demonstrated the effectiveness of TIKTAG-v2 devices in opposition to the Google Chrome browser, notably the V8 JavaScript engine, opening up the trail to exploiting reminiscence corruption vulnerabilities within the renderer course of.
Supply: arxiv.org
Trade response and mitigations
The researchers reported their findings to the impacted entities between November and December 2023 and acquired a typically optimistic response, although no quick fixes have been carried out.
The technical paper printed on arxiv.org proposes the next mitigations in opposition to TIKTAG assaults:
- Modify {hardware} design to forestall speculative execution from modifying cache states primarily based on tag test outcomes.
- Insert hypothesis boundaries (e.g., sb or isb directions) to forestall speculative execution of vital reminiscence operations.
- Add padding directions to increase the execution window between department directions and reminiscence accesses.
- Improve sandboxing mechanisms to limit speculative reminiscence entry paths strictly inside secure reminiscence areas.
Whereas ARM acknowledged the seriousness of the scenario and printed a bulletin just a few months again, it doesn’t take into account this a compromise of the characteristic.
“As Allocation Tags should not anticipated to be a secret to software program within the deal with house, a speculative mechanism that reveals the right tag worth shouldn’t be thought of a compromise of the ideas of the structure,” reads the ARM bulletin.
Chrome’s safety crew acknowledged the problems however determined to not repair the vulnerabilities as a result of the V8 sandbox shouldn’t be supposed to ensure the confidentiality of reminiscence knowledge and MTE tags.
Furthermore, the Chrome browser doesn’t at the moment allow MTE-based defenses by default, making it a decrease precedence for quick fixes.
The MTE oracles within the Pixel 8 machine have been reported to the Android safety crew later, in April 2024, and have been acknowledged as a {hardware} flaw qualifying for a bounty reward.