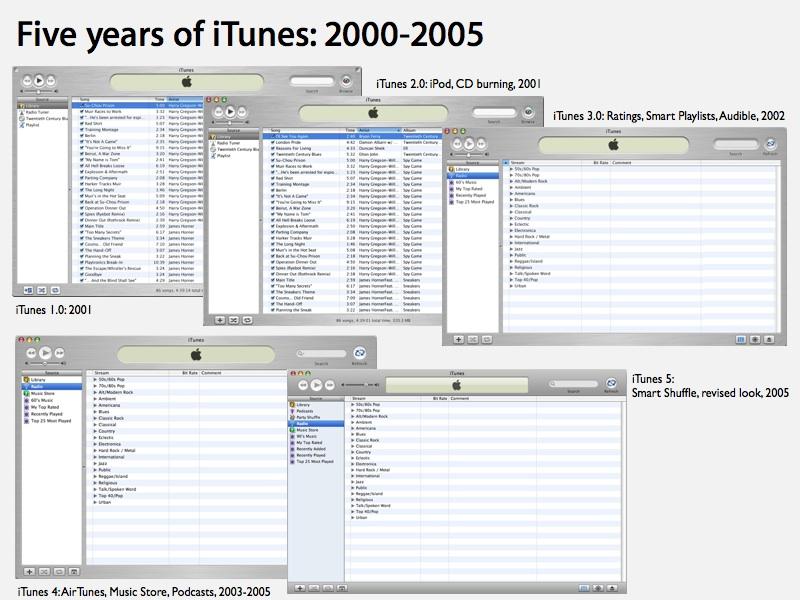
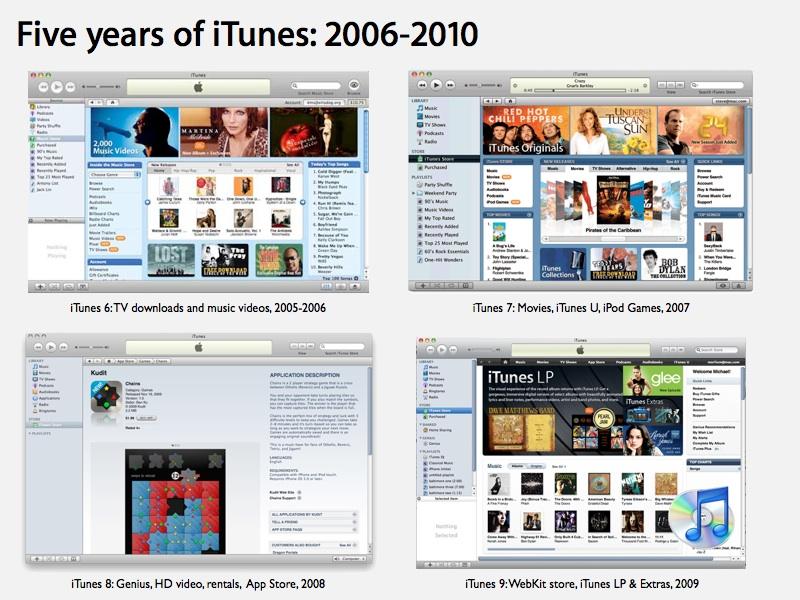
To have fun 2025, I compiled Apple’s high ten main areas of innovation over the previous 25 years. Let’s take a look at the selections that led to this blockbuster success of the iPod and implications for brand spanking new merchandise in the present day.
The primary phase mentioned Apple’s 2000 launch of Mac OS X Public Beta, its most vital innovation within the final 25 years. The second phase centered on Apple’s reinvented retail operations. The third phase appears at iPod.
Apple cheats dying with a technique of innovation
If the “Apple Laptop” of the brand new millennium had solely centered on retrofitting the Macintosh to promote as its principal cash maker, it’s unlikely it could have survived a decade. On the time, Apple was promoting about 3 million Macs yearly. Apple was beleaguered.
Apple was additionally innovating. It had launched a sequence of properly acquired Mac merchandise, from the unique 1998 iMac G3, to the 1999 iBook, the 1999 “supercomputer” Energy Mac G4 and the titanium PowerBook G4 in early 2001. Cautious optimism was starting to sprout concerning the firm’s flip round beneath the preliminary years of Steve Jobs‘ charismatic and pragmatic reinvention of the corporate.
Considerations arose from darkish clouds throughout the Dot Com growth. Apple’s PowerMac G4 Dice, launched simply because the market peaked, confronted tepid gross sales. The inventory market crash additional affected demand. The flamboyant however dear Dice was a lower than compelling selection for a lot of core prospects in artistic markets or training. Apple misjudged its potential viewers proper earlier than its patrons had been more and more pressured to retreat away from luxurious purchases.
It appeared there was an inherently restricted potential viewers for Macs, and that was an issue for Apple. Rising competitors from low cost commodity PCs additional eroded gross sales prospects for high-end desktop and laptop computer computer systems. Apple actually wanted one thing to goose its gross sales.
To spice up Mac demand amongst professionals, Jobs’ Apple centered on producing unique new software program titles. Apple acquired Remaining Reduce from Macromedia in 1998 and relaunched it as Remaining Reduce Professional in 1999. Three years later, it acquired Logic from Emagic. Considered one of Apple’s biggest improvements was to leverage nice software program to assist promote its {hardware}.
On the identical time, Apple embarked upon an identical technique for house and training customers, launching iMovie in 1999 as a simple to make use of film editor alongside the New iMac DV. That very same 12 months, Apple purchased SoundJam MP from developer Casady & Greene, with the intent to show the music library software program into iTunes.
Apple pursued an revolutionary technique of launching artistic, straightforward to make use of new first get together apps to drive curiosity in its Mac {hardware}. This created a “digital hub” for customers, the place the Mac reworked from being only a browser and e mail machine right into a artistic heart for a person’s more and more linked “digital life” of films, photographs and music.
Apple wasn’t making super revenues from promoting its software program. These new titles existed primarily to drive Mac adoption. However having its personal bundled software program opened up new alternatives for the corporate, with the primary clearly being its new accent for iTunes that acted as a distant “pod” for taking desktop music anyplace.
Apple did not invent moveable music. Whereas the corporate did pioneer key components of desktop enhancing of digital audio and even digital video a decade earlier with QuickTime within the early 90s, its reliance on third get together builders to really make use of its QuickTime middleware to ship highly effective Mac apps started to falter with the discharge of Microsoft’s Home windows 95.
The artistic instruments trade, together with Adobe and Macromedia, started to give attention to quantity PC prospects with Home windows variations of their merchandise. Microsoft was additionally doing all it may to scuttle Apple’s QuickTime. It pushed its companions to cease utilizing and distributing Apple’s software program in favor of its personal. Microsoft even stole code from Apple’s QuickTime to enhance the efficiency of its personal media software program for Home windows.
On the music entrance particularly, Microsoft additionally started to pursue a technique of tying all business music to its personal proprietary gamers through its Digital Rights Administration safety software program. It would not matter how engaging Apple’s music {hardware} and software program had been if its far more highly effective PC competitor managed the spigot of all licensed music and will flip this off for Mac customers on a whim.
Apple’s iTunes technique acknowledged this menace. It tried to create a substitute for Microsoft’s Home windows Media and Sony’s parallel efforts to lock up business music with its personal DRM. In 2001, iTunes launched with the promoting marketing campaign “Rip. Combine. Burn,” alongside a brand new iMac with Apple’s first CD-RW optical drive.
Apple wasn’t first to put in rewritable disc recorders in a PC, however the mixture of iTunes’ ease of use inside the general Mac bundle resonated with customers. A part of Apple’s technique of innovation was merely recognizing what individuals wished to do, and doing the work to make that simpler.
By liberating customers to ingest their current CD libraries and burn chosen playlists onto commonplace CDs they might use anyplace, an iMac operating iTunes provided a vastly higher expertise than the advanced and restrictive rule units Microsoft and Sony had been trying to push on customers.
Microsoft was catering to its music companions, providing them broad flexibility with Home windows Media to restrict how customers may use their very own songs. Sony was largely working to hyperlink media gross sales to its personal {hardware}, notably its new MiniDisc moveable format that inspired customers to purchase one other new media format. It even restricted what customers may placed on their very own MDs.
Apple was promoting a superior expertise on to its prospects. Its whole technique was designed explicitly for its prospects, not for its companions. Many recording labels had been initially hostile to the idea of customers making copies of their very own music, although music piracy had already develop into properly established. Whereas Microsoft and Sony had been attempting to place that cat again into the bag, Apple was providing a wholly new means to consider music— initially to promote Macs, then to promote its personal music participant.
MP3 gamers had already develop into standard gadgets by the late 90s, however they’d a couple of important shortcomings. As a way to retailer greater than just some songs, they both had to make use of rewritable optical media or a standard arduous drive, each of which had been cumbersome and fragile.
Navigating the music on such a tool rapidly grew to become unwieldy as track libraries expanded. The connectivity between gamers and a PC able to copying track recordsdata to the moveable gadget was additionally problematically gradual. Battery life was a problem. Strong state storage was nonetheless too costly to make use of liberally.
Apple happily had a wide range of options already. Its work with digital video had resulted in Macs getting quick Firewire ports beginning in 1999. The brand new iTunes provided a strategy to arrange and type recordsdata on a robust laptop, and to use metadata to assist navigate giant libraries on an exterior gadget.
Toshiba had developed a compact arduous drive it was buying round to patrons with out discovering a lot curiosity. In search of to enter the music participant enterprise, Apple launched a crew beneath Tony Fadell to show the idea into a sexy product.
Apple’s restricted expertise in shopper merchandise outdoors of Macs meant that a lot of the iPod’s particulars had been contracted to others. PortalPlayer software program and a UI system by Pixo helped Apple focus its inside work on the {hardware} expertise and its integration with iTunes. The consequence was an opulent 5MB moveable system with quick FireWire connectivity. Cumbersome HD and optical gamers out of the blue seemed actually quaint, and their serial or USB 1.1 speeds felt anemic as compared.
Apple additionally benefitted from its prior decade of expertise with laptops and batteries, however it nonetheless needed to develop important components of iPod’s moveable {hardware} from scratch, or depend on third get together chips and different parts. The true product Apple was promoting was the iPod expertise.
Immediately, Apple has the dimensions and assets to customized develop its personal software program from apps to the OS to the underlying firmware. It designs its personal {hardware} proper all the way down to the silicon in lots of instances. However what Apple continues to promote remains to be an general expertise.
The revolution of a transportable Apple
Preliminary gross sales of iPods had been, by in the present day’s requirements, comparatively restricted. In 2002, its first fiscal 12 months of iPods, Apple had offered fewer than 400,000 items. In 2003 it offered practically one million. However in 2004 that determine jumped to 4.4 million, adopted by greater than 22 million in 2005 and nearly 40 million in 2006.
The exploding development and enlargement of the iPod household of gadgets radically shifted Apple from being a fringe laptop maker to being a really excessive quantity gadget producer. Apple was not solely promoting unbelievable volumes of gadgets, but additionally shopping for up huge strategic reserves of parts similar to RAM and arduous drives.
Apple’s excessive quantity purchases for iPod additionally helped improved its negotiating energy for Mac parts. It additionally took classes realized from iPod to its Mac fashions. Expertise with iPod additionally helped to commodify parts of the Mac.
Whereas FireWire was initially a lot quicker than USB 1.1, Apple rapidly included early help for USB 2.0 to assist promote iPods to Home windows customers. It additionally ported iTunes to PCs, giving many Home windows customers their preliminary introduction to the Apple world.
iPod additionally performed a key position within the firm’s newly constructed Apple Shops. It introduced in a wholly new group of customers and launched them to the Mac. It additionally helped set up the Apple Retailer as a showplace for normal new introductions of iPod fashions.
Excessive quantity iPod gross sales additionally helped Apple accomplice with third get together accent makers. Apple’s personal clumsy makes an attempt to ship equipment, starting from iPod Socks to iPod HiFi, made it important for the corporate to work with smaller builders who may check out a variety of choices to suit customers wants.
Did it need to be iPod?
On reflection, Apple’s monumental success with iPod and all of its surrounding improvements, the halo it forged over the Mac, and the inspiration it helped lay for Apple’s forthcoming moveable and wearable merchandise, all appear as if they might have been utilized anyplace.
Why did Apple choose moveable music as its focus, quite than say, digital pictures? Was iPod simply the success Apple created from of a random strategic selection and simply numerous intelligent advertising? Might the identical quantity of effort simply as properly have been invested into an “iCam” with the identical outcomes?
The Apple of the Nineteen Nineties had truly already pursued a number of experiments in moveable gadgets classes. It most famously started work on a “digital assistant” that grew to become the Newton MessagePad in 1994.
Apple spent super funds creating customized OS software program, a singular programming surroundings, revolutionary stylus-based apps and companies, and even bespoke ARM chips suited to the cellular gadget.
Somewhat than being a smash success, Newton truly suffered from being excessively bold— it wasn’t fairly completed at launch and value an excessive amount of to be broadly engaging for what it may do.
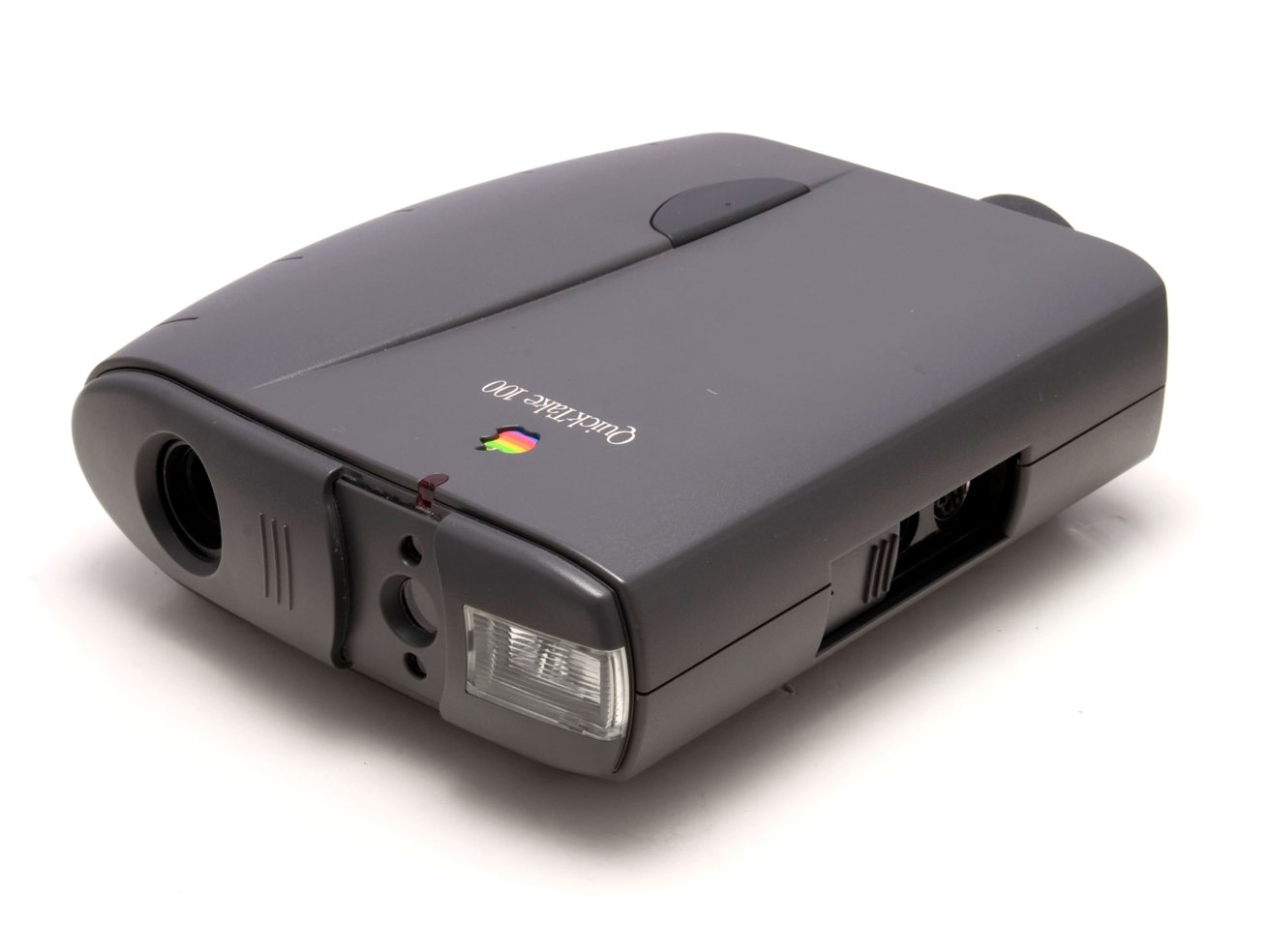
It is much less well-known that Apple additionally pioneered digital pictures, working with Kodak to ship QuickTake cameras beginning in 1994. Like iPod later would, this product additionally leveraged Apple’s multimedia software program to handle and arrange its digital recordsdata. Not like iPod, Apple’s QuickTake cameras arrived with out the showcasing energy of its forthcoming Apple Shops.
Like Newton, QuickTake cameras had been fairly costly and restricted in what they might truly accomplish. Additionally like Newton, the QuickTake line was rapidly discontinued by Jobs after his return to Apple as a way to simplify operations.
What prevented Apple from returning to digital cameras in 2001, quite than shifting its cellular focus to digital music with iPod?
Partly, digital cameras provided Apple lots much less business alternative. By 2001, digital imaging know-how had improved considerably, however a lot of the worth within the trade was being captured by excessive finish digicam makers promoting skilled digital cameras priced nearer to $8,000.
Professional pictures customers may afford to learn from the benefits of capturing digitally, however they represented a a lot smaller market with restricted potential for development.
Shopper digital cameras priced across the $800 vary of QuickTake provided restricted benefits over extra inexpensive, commonplace movie cameras. High quality at that value level was nonetheless struggling to catch as much as movie, whereas movie photographs may already be digitized after they had been developed, even placed on a Picture CD to be used with computer systems.
Apple’s digital digicam rivals had been additionally lots higher established and competent than makers of MP3 gamers. Apple had much less to supply when it comes to enhancing upon the expertise of cameras in comparison with what it may do to make a greater MP3 participant.
Amongst digicam makers, there have been a number of very competent, extremely aggressive producers already properly versed in superior optics and more and more subtle customized chips and digital sensors, and had been adept in delivering common usability. These makers had been additionally already earning money from their movie cameras.
MP3 manufacturing was scattered throughout smaller gamers making cumbersome optical or arduous drive gamers, or very restricted Flash Reminiscence gadgets. USB had arrived however was nonetheless gradual. It might be straightforward to liken the MP3 market in 2001 to the place cellphones had been in 2007, or good watches in 2014, or VR headsets in 2024.
iPod’s music provide
One other strategic aspect important to iPod was lacking out there for digital pictures. Whereas finish customers may create their very own music simply as they’d take their very own photographs, most music listeners can be attempting to hearken to commercially recorded music.
Digital cameras weren’t equally providing to play TV and flicks or providing customers a library of inventory pictures to view. In truth, a significant purpose why Apple pursued iPod was the parallel potential provided by what would develop into the iTunes Music Retailer. There was no analog for digital cameras.
Immediately we could consider the iTunes Music Retailer as a significant new revenue heart for Apple, however its authentic impetus wasn’t making a number of cash. As a substitute, a lot of Apple’s technique for iTunes was merely geared toward making a parallel supply for business content material for Macs and iPods.
Apple was centered on promoting {hardware} and incomes nearly all of its earnings from Macs and later iPods. It incessantly acknowledged, initially, that it was operating iTunes Music Retailer at break-even.
Round 2000, the digital music trade was being held again by Microsoft and Sony’s rival efforts to push their very own DRM. If Microsoft and Sony had succeeded in locking up commercially recorded music with their DRM, the marketplace for all of Apple’s {hardware} would have been imperiled.
There’s restricted appreciation of Apple’s expertly delicate dance over the 2000s— first embracing ripped CDs, then transitioning to single monitor music gross sales within the iTunes Music Retailer, after which introducing FairPlay DRM to appease music labels with out turning off its prospects.
The event of iTunes in parallel with iPod required a wholly new mind-set about digital content material that’s exceptional sufficient to deserve its personal high ten article.
iPod legacy
Earlier than trying on the iTunes Retailer, think about the lasting legacy of Apple’s funding and innovation in its digital music {hardware}.
Apple’s preliminary, incremental gross sales of iPods helped the product to quickly enhance. Between 2001-2003, shopper demand for extra storage took the unique 5GB iPod to 10GB after which 20GB fashions, facilitated by the shrinking sizes and growing densities of arduous drives.
Apple did not develop these arduous drive mechanisms. As a substitute it relied on a sequence of aggressive suppliers all in search of to ship higher parts to win Apple’s excessive quantity enterprise. Immediately, Apple equally would not create all of its personal parts. It depends on Sony and Samsung for cameras and shows, and makes use of storage and RAM developed by others.
Whereas Jobs was credited with the imaginative and prescient of what iPod ought to appear like and the way it ought to really feel, it was Apple’s operations govt Tim Prepare dinner that brokered the corporate’s unique part offers, giving it aggressive benefits over different firms in search of to enter the music participant market.
If Apple had tried to construct every little thing by itself, it could find yourself closely invested in excessive threat industries like reminiscence and sensors identical to Sony and Samsung, and reliant on others to assist it promote what it had developed.
As a substitute, Apple has chosen sure strategic areas the place it might beat the remainder of the trade— similar to in the present day’s Apple Silicon— whereas counting on many commodity elements superior by others. A lot of the innovation was pushed by gathering the understanding of the place it may add worth, and the place it may lean on companions.
Apple not solely negotiated large provider offers for iPods, but additionally expanded gross sales of iPods with key companions. In 2004, the considerably bigger HP started licensing Apple’s iPod as an alternative of creating its personal product.
That very same 12 months, Microsoft rushed out its personal Home windows Transportable Media Middle and started licensing its designs for Transportable Media Gamers with Samsung, Inventive, iRiver and different PC and gadget makers.
Microsoft’s failure to beat Apple’s iPod with its “Home windows” branded alternate options forged the primary critical doubts over Microsoft’s supremacy within the tech world. The corporate sealed that destiny with the Zune, launched in 2006, even earlier than Apple’s iPhone obliterated Microsoft’s different cellular efforts. This dramatically shifted views on Macs as properly.
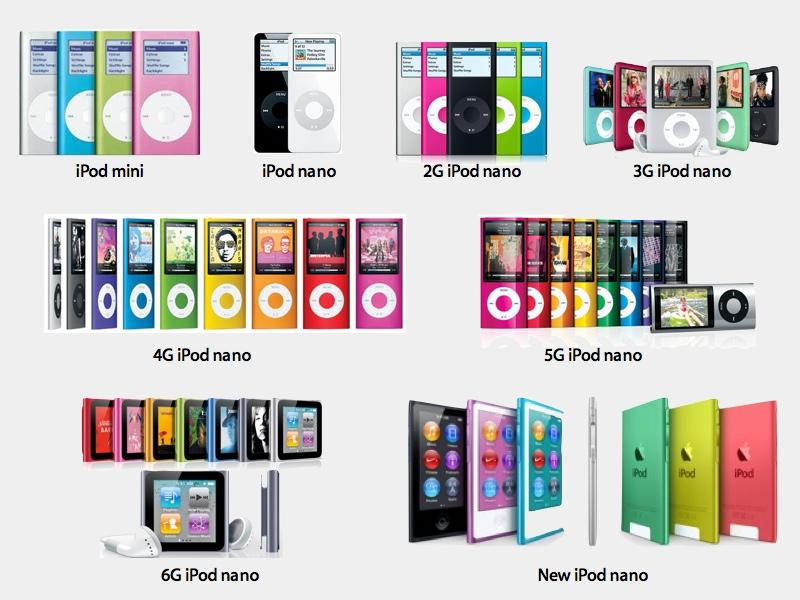
Apple did not simply sit again and rake in iPod earnings. As a substitute, it relentlessly innovated in creating new tiers of iPods. In 2004 Apple launched iPod mini utilizing a fair smaller, thinner arduous drive. It was provided it a number of colours as a extra inexpensive possibility. Its excessive quantity gross sales continued to maintain Apple a aggressive part purchaser and honed its design capabilities.
Apple’s more and more exact and exacting design and manufacturing capability significantly improved the Mac as properly, serving to to remodel the iMac right into a tightly built-in bundle behind an LCD. This additionally helped Apple to more and more enhance upon the dimensions and sturdiness of MacBooks and their batteries and storage.
In 2005 Apple launched iPod nano utilizing Flash Reminiscence as an alternative of a tough drive. The corporate most well-liked to quickly cannibalize its personal product lineup to remain aggressive and revolutionary. The nano accelerated the mini’s give attention to style and helped Apple shift away from tech specs into being an aspirational model.
Apple’s mass consumption of Flash Storage for years of iPod nano helped put together the corporate to pioneer the usage of SSD storage within the forthcoming MacBook Air in 2008.
Alongside iPod nano in 2005, Apple launched iPod Shuffle, an ultra-portable model with no display screen, emphasizing simplicity and affordability. Its smaller measurement and random music playback centered on a brand new position in operating and exercises.
Parallel with these two new smaller instructions for iPod, 2005’s iPod Video shifted the excessive finish iPod into being a extra subtle multimedia gadget for presenting TV reveals, motion pictures and music movies. That performance expanded Apple’s media leverage past music and acted as a shoulder for iPhone to face on at its launch two years later.
Not solely did iPod blossom into iPhones, however the wrist-wearable sixth era iPod nano successfully impressed the later improvement of Apple Watch, fully shifting the corporate from being a tool maker to being a way of life model promoting luxurious wearables.
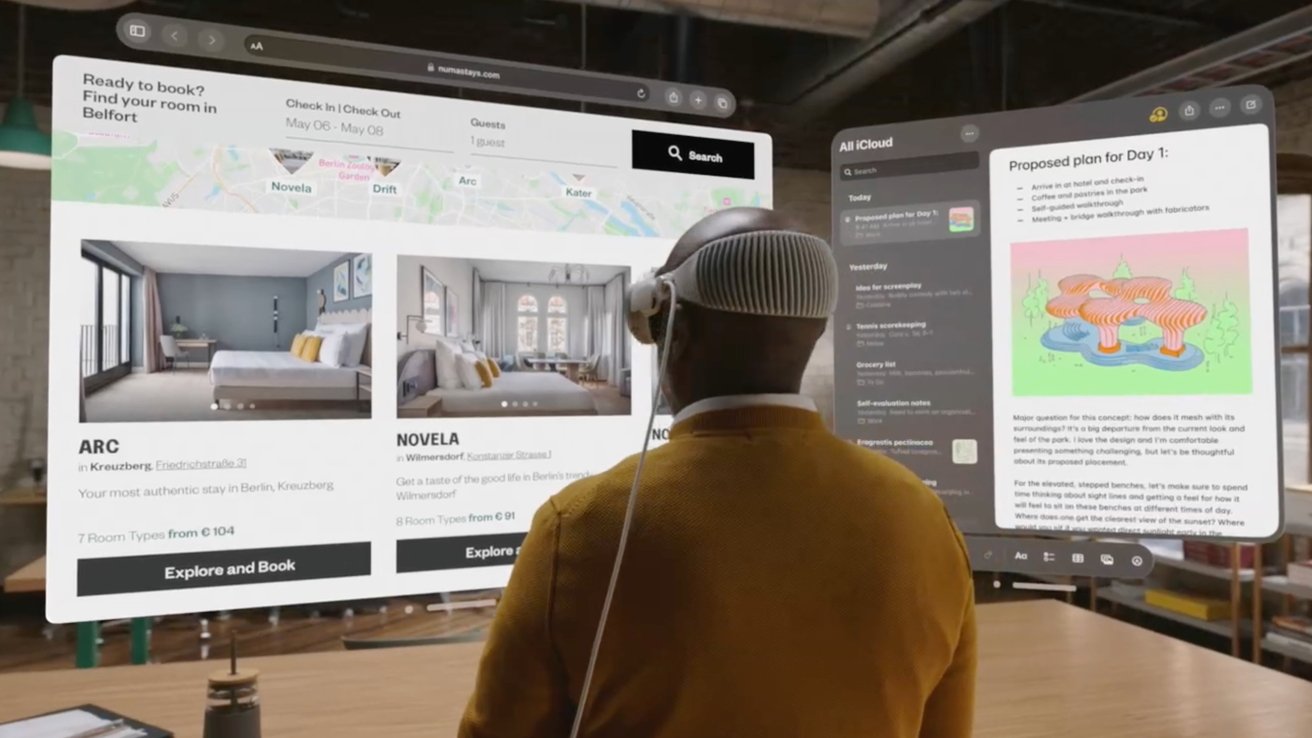
You might even make the case that iPod performed a task in defining in the present day’s Imaginative and prescient Professional. Not like many others within the AR/VR area, Imaginative and prescient Professional was created as a standalone, self contained gadget that may sync along with your different gadgets as a peer, quite than being tethered from them as a mere peripheral.
iPod outlined the last decade of the 2000s. It formed the event of Apple’s international provide chains for shopper gadgets, and helped revolutionize how we use digital media. It survives, not as {hardware}, however as software program performance. Its {hardware} wasn’t even formally discontinued till 2022.
iPod wasn’t one single innovation or invention however quite a continuation of strategic developments that efficiently pursued growing areas of utility, a number of value factors, and radically shifting kind elements.
Think about if the world had paid consideration to early critics pouting about lacking options or had cared that early gross sales took a while to actually shift the computing panorama and alter every little thing!
That gives some perspective for Imaginative and prescient Professional in the present day, at a time when Apple has way more market energy and the power to develop its personal customized silicon and even produce its personal bespoke immersive content material. Imaginative and prescient Professional is, successfully, an iPod on your eyes.